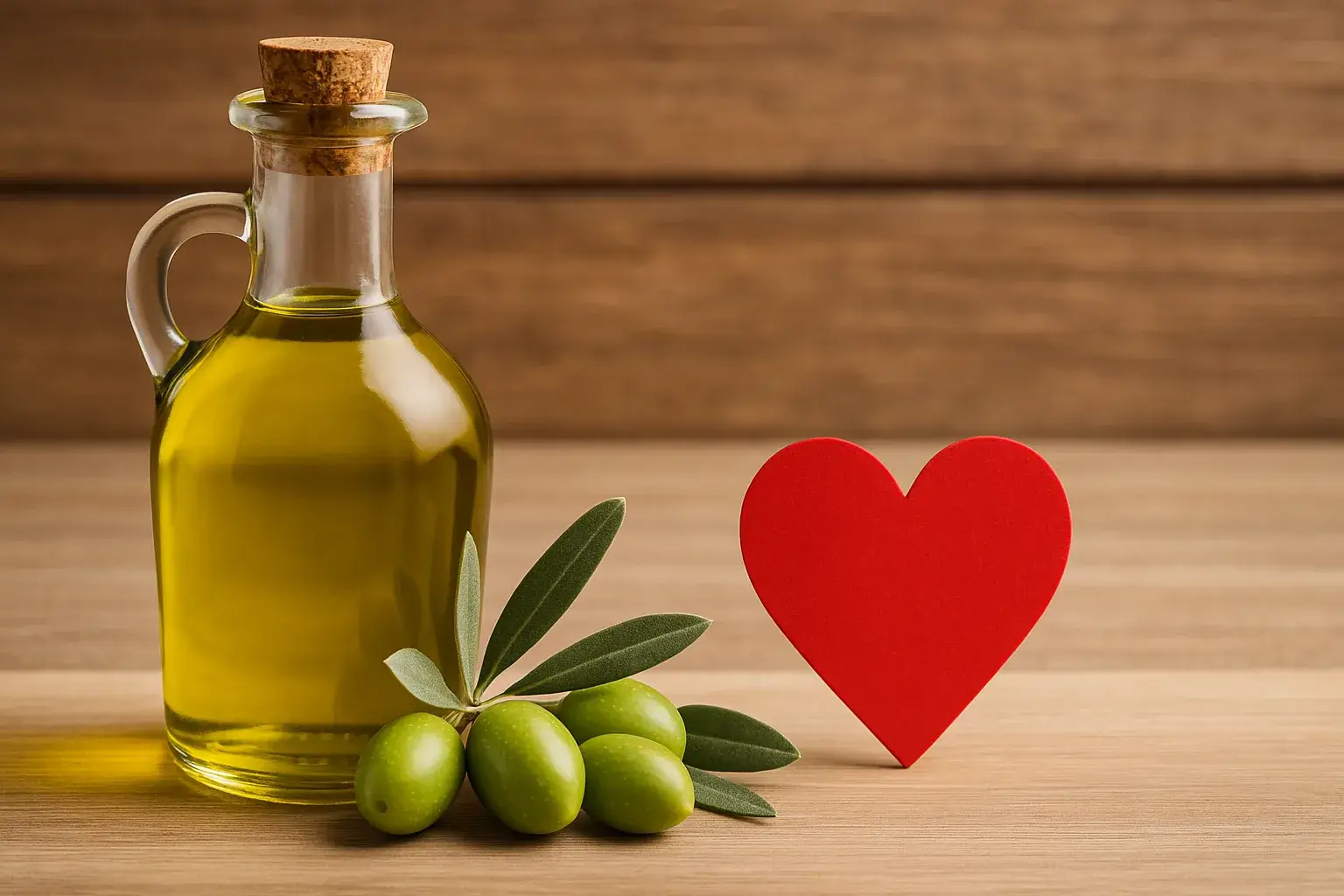
Olive Oil: Key to Heart Health
- Olivia Hart
- Health , Nutrition , Wellness
- May 29, 2025
Table of Contents
Fast Facts: Olive Oil & Heart Health (TL;DR)
- Heart Protector: Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) is a cornerstone of the heart-healthy Mediterranean diet, offering significant cardiovascular benefits.
- Lowers Risk: Major studies, like the PREDIMED trial, demonstrate that a Mediterranean diet with EVOO reduces the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and cardiovascular death [1].
- Mechanism: EVOO boosts ‘good’ HDL cholesterol, combats inflammation through compounds like oleocanthal, and provides potent antioxidants to protect blood vessels [2, 3].
- Daily Dose: Incorporating 1-2 tablespoons of high-quality, cold-pressed EVOO daily can support vascular health.
- Choose Wisely: Opt for cold-pressed Extra Virgin Olive Oil for the highest concentration of beneficial compounds.
For centuries, the Mediterranean diet has been celebrated for its profound health benefits, consistently linked to longevity and robust heart health. While this dietary pattern emphasizes a rich variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, fish, and legumes, scientific inquiry increasingly points to one component as a standout contributor to its cardiovascular prowess: extra virgin olive oil (EVOO). This golden liquid is far more than a simple culinary ingredient; it’s a potent functional food with scientifically validated properties that support vascular health, combat inflammation, and promote long-term well-being.
Unveiling the Cardioprotective Power of EVOO
While the synergy of the entire Mediterranean diet is undoubtedly beneficial, research highlights extra virgin olive oil as a primary driver of its remarkable cardiovascular advantages. It’s not just about replacing less healthy fats; EVOO possesses unique compounds that actively work to protect your heart and blood vessels. Understanding the “benefits of extra virgin olive oil for heart” involves looking at compelling scientific evidence.
The Landmark PREDIMED Study: A Turning Point

One of the most influential studies in this field is the PREDIMED (Prevención con Dieta Mediterránea) trial, published in The New England Journal of Medicine [1]. This large, long-term, randomized clinical trial investigated the effects of a Mediterranean diet supplemented with either EVOO or nuts, compared to a low-fat control diet, on primary cardiovascular prevention in individuals at high cardiovascular risk.
Key Findings from PREDIMED:
The results were groundbreaking:
- Reduced Cardiovascular Events: Participants following the Mediterranean diet supplemented with extra virgin olive oil experienced a significant reduction in the risk of major cardiovascular events (myocardial infarction, stroke, or death from cardiovascular causes) compared to those on the low-fat diet.
- Support for EVOO’s Role: While the nut-supplemented group also saw benefits, the findings robustly supported the inclusion of EVOO as a key element for cardiovascular protection.
- Beyond General Diet Advice: This study provided strong evidence that the type of fat, not just the total amount of fat, is critical for heart health, underscoring the “scientific evidence olive oil heart health.”
These findings suggest that extra virgin olive oil is a vital dietary component for those seeking to proactively manage their cardiovascular health and combat the processes that lead to arterial damage, such as atherosclerosis.
How Extra Virgin Olive Oil Fortifies Your Heart
The remarkable heart-health benefits of EVOO stem from its rich composition of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), primarily oleic acid, and a potent array of polyphenols and antioxidants [2]. These compounds work synergistically:
1. Optimizes Cholesterol Profile
- EVOO helps increase levels of HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, often termed “good” cholesterol. HDL cholesterol plays a crucial role in reverse cholesterol transport, carrying excess cholesterol from the arteries back to the liver for removal [4].
- It can also help lower levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol (“bad” cholesterol) and, importantly, its polyphenols protect LDL particles from oxidation—a key initiating step in the development of atheromas (arterial plaques). This directly addresses “how olive oil reduces cholesterol” in a multifaceted way.
2. Combats Inflammation
- Chronic inflammation is a silent culprit in many diseases, including cardiovascular disease where it contributes to endothelial dysfunction (damage to the inner lining of blood vessels).
- EVOO contains potent anti-inflammatory compounds. One notable example is oleocanthal, a polyphenol that exhibits anti-inflammatory properties similar to ibuprofen [3]. This makes “olive oil and inflammation cardiovascular” a key area of its protective action.
3. Delivers Powerful Antioxidant Protection
- The polyphenols in EVOO, such as hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein, are powerful antioxidants. They neutralize free radicals, unstable molecules that cause oxidative stress.
- Oxidative stress damages cells, contributes to arterial stiffness, promotes plaque formation, and accelerates the progression of cardiovascular disease.
4. Supports Endothelial Function
- A healthy endothelium is crucial for maintaining vascular tone, proper blood flow, and preventing clot formation.
- The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of EVOO help protect the endothelium, ensuring blood vessels remain flexible and responsive.
Incorporating EVOO: Practical Advice for Optimal Heart Health
Harnessing the “benefits of extra virgin olive oil for heart” is simple. Aim to include 1–2 tablespoons (approximately 15-30 ml) of high-quality extra virgin olive oil in your daily diet:
- Salad Staple: Use EVOO as the base for your salad dressings.
- Flavor Enhancer: Drizzle it over steamed or roasted vegetables, whole-grain bread, pasta, or cooked grains.
- Healthy Fat Boost: Add a swirl to soups or even smoothies.
- Cooking Choice: Use it for sautéing at moderate temperatures. While EVOO has a lower smoke point than refined oils, quality EVOO is suitable for most everyday cooking methods.
BioBrain Tip: Always prioritize cold-pressed, extra virgin olive oil. This ensures minimal processing and the highest concentration of beneficial polyphenols and antioxidants. Store it in a cool, dark place to maintain its quality. “Best olive oil for heart disease prevention” is invariably EVOO.
EVOO: More Than Food, It’s Cardiovascular Medicine
Extra virgin olive oil transcends its role as a mere dietary fat. Its unique biochemical makeup positions it as a natural, potent tool for maintaining and even helping to restore vascular health. Its demonstrated ability to:
- Favorably modulate cholesterol levels
- Reduce systemic inflammation
- Protect against oxidative damage
- Support endothelial integrity
Collectively contribute to “preventing atherosclerosis with olive oil” and make it an indispensable component of a heart-protective lifestyle.
Your Heart Will Thank You
If enhancing your cardiovascular well-being is a priority, the robust scientific evidence supporting extra virgin olive oil cannot be ignored. It’s not just a traditional food; it’s a natural elixir for your arteries, backed by modern science.
By consciously incorporating high-quality EVOO into your daily meals, you’re not just adding flavor—you’re investing in your long-term heart health, potentially warding off disease and supporting a more vibrant life.
Frequently Asked Questions (Q&A)
Q1: What are the main cardiovascular benefits of extra virgin olive oil?
Q2: How does olive oil affect cholesterol levels?
Q3: Is all olive oil equally good for heart health?
Q4: How much olive oil should I consume daily for heart benefits?
Q5: Can olive oil help reduce inflammation related to heart disease?
Disclaimer
The information provided on BioBrain is intended for educational purposes only and is grounded in science, common sense, and evidence-based medicine. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before making significant changes to your diet, exercise routine, or overall health plan.
References
- Estruch R, Ros E, Salas-Salvadó J, et al. (2018) "Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet Supplemented with Extra-Virgin Olive Oil or Nuts."
- Gorzynik-Debicka M, Przychodzen P, Cappello F, et al. (2018) "Potential Health Benefits of Olive Oil and Plant Polyphenols."
- Beauchamp GK, Keast RS, Morel D, et al. (2005) "Phytochemistry: ibuprofen-like activity in extra-virgin olive oil."
- Mayo Clinic Staff "HDL cholesterol: How to boost your 'good' cholesterol."
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2004) "Qualified Health Claims: Letter of Enforcement Discretion - Olive Oil and Reduced Risk of Coronary Heart Disease (Docket No. 2003Q-0559)."
- American Heart Association (2021) "Monounsaturated Fat."
Tags :
- Olive oil
- Heart health
- Cardiovascular
- Hdl cholesterol
- Atherosclerosis
- Evoo
- Antioxidants
- Inflammation
- Diet
- Wellness
- Extra virgin olive oil
- Mediterranean diet